au sommaire
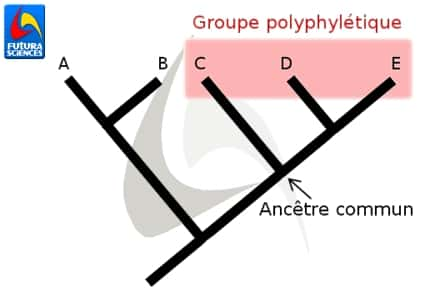
La sélection rouge représente un groupe polyphylétique. Il inclut les taxons C à E mais pas leur ancêtre commun. © Quentin Mauguit, Futura-Sciences
Dans la classification des êtres vivants, un groupe ou taxon est dit polyphylétique lorsque qu'il regroupe des taxons en excluant leur ancêtre commun.
La polyphylie s'oppose ainsi à la monophyliemonophylie et la paraphylieparaphylie.
Sur le schéma ci-dessous, la sélection en rouge représente un groupe polyphylétique. Les taxons C à E ont un ancêtre commun mais il ne fait pas partie du groupe.